With Windows Server 2012 and 2016, Microsoft integrated a wide range of innovations in its server operating system. In comparison with Windows Server 2019, the focus is now on improving these innovations and adding practical refinements.
Index
Windows Server 2019 – What’s new?
Upgrade intervals of Windows Server 2019
Already in mid 2017 the following Windows Server release channels were available:
Semi Annual Channel (SAC): Microsoft publishes releases for Windows Server products through the Semi-Annual Channel. New releases in the SAC are only available as Server Core and the container image of the Nano server. The support commitment is limited to the next 18 months only. The releases in the SAC are primarily intended for containers.
Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC): Windows Server 2019 is a release in the LTSC. The support commitment runs for 10 years as usual.
Desktop Experience
Furthermore, the installation option “Desktop Experience” only supports releases in the LTSC. This means that the operating system can be installed with a graphical interface. The graphical interface is very similar to the respective release of the client OS (Windows 10).
Desktop Experience should be used above all for Remote Desktop. For all other functions, even Exchange 2019, the server core is sufficient.
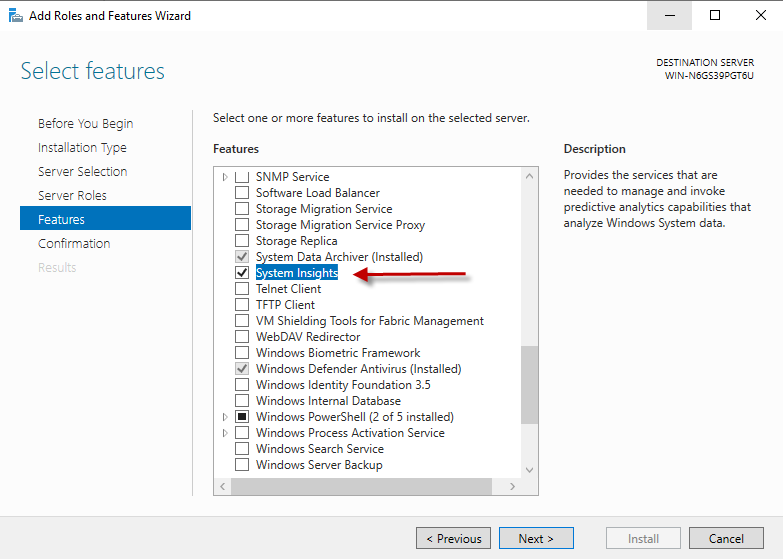
System Insights
Security
Windows Defender ATP
Windows Server 2019 focused particularly on security issues. It introduced an antimalware service called “Windows Defender ATP”. It connects with the security infrastructure in Azure.
Furthermore, the new “virus scanner” has an exploit-protection with a number of intrusion prevention functions.
Notably, Microsoft made visible progress in recent years in this area.
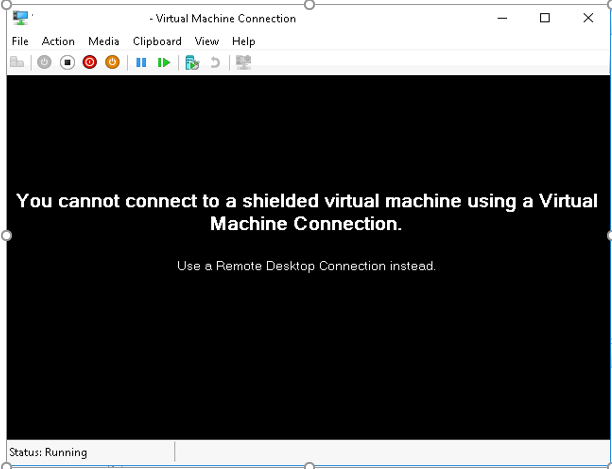
Shielded VMs
Now the improvements:
- The protection component (Host Guardian Service) does not have to be continuously accessible. However, it can be offline for a short time. This makes sense for the operation of VMs at other locations.
- improved troubleshooting for RDP connections in VMs
- Linux can be used as special protected VMs
View of a VM from the perspective of the hoster (virtual admin)
Storage
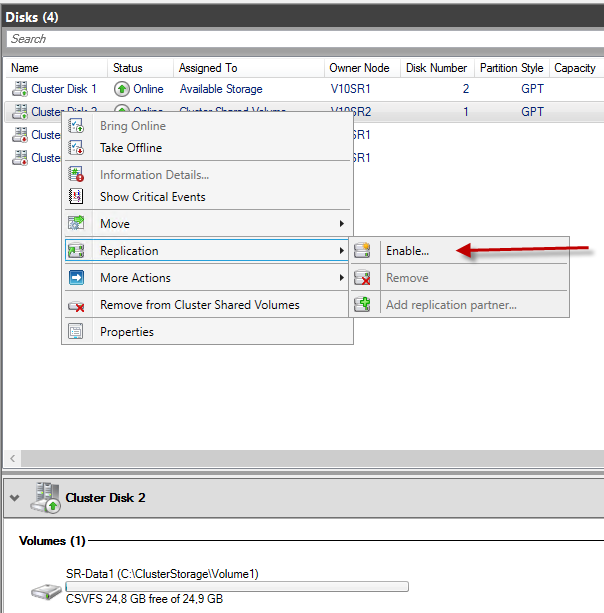
Storage Replica light
With Windows Server 2016, Microsoft introduced the “Storage Replica” feature. It enabled a block-based replication of data volumes between servers, clusters, or within clusters. Thus, a geocluster or metro cluster was only possible with the use of a Windows Server. This replication can be synchronous or asynchronous. However, this feature was reserved for the Datacenter edition only.
New with Windows Server 2019: The feature exists – in a slimmed down form – also in the standard version. However, only a volume up to 2TB in size can be replicated.
Storage Migration Service
The Storage Migration Service allows storage migrations from legacy Windows systems or non-Windows systems to migrate file shares to Windows Server 2019 or Azure.
It migrates all data, shares and their configuration, permissions, users, groups, attributes, alternate data streams, IP addresses and computer names, irrespective of the data being used or not.
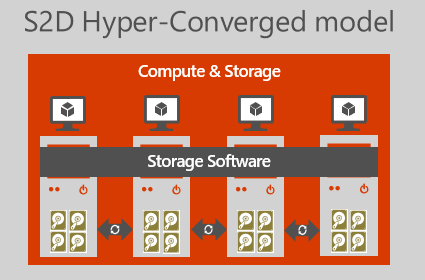
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
Storage Spaces is a Windows Server 2012 and 2016 enhanced feature for delivering highly available and highly scalable storage at a cost-effective price by implementing industry-standard hardware. This can significantly reduce the price per terabyte of data stored, compared to a traditional SAN.
Starting with Windows Server 2016, the system was able to be converged and hyperconvergent. This means, that the storage hard disks no longer runs in external JBOD enclosures. And within normal server hardware as internal hard disks, that virtualization and storage can be performed on one and the same hardware.
The most important advantages:
- 4 petabytes can be stored per cluster
- Mirror Accelerated Parity for higher performance
- Improved resilience in 2-node clusters
- Support for persistent memory e.g. Intel Optane
Improvements ReFS
ReFS is the file system introduced with Windows Server 2012 for extremely high data volumes, high integrity and support for extremely long path and file names (among others)
With Windows Server 2019, ReFS supports deduplication and compression of data.
This means increasing the amount of data stored by a factor of 2-10.
Changes in the cluster
- Clusters are usually integrated into an AD domain. If you wanted to move a cluster into a new domain, you would have to destroy the cluster first and then rebuilt it in the other domain.
- The File Share Witness no longer needs to be an AD member.
Conclusion
Microsoft is introducing a whole host of new features and enhancements to its server operating system with Windows Server 2019. The number of truly innovative innovations, which can mean significant improvements for companies of all sizes, remains manageable.
After recalling a bad cumulative update, I can advise you to introduce Windows Server 2019 as part of the normal upgrade process. It looks like an improved and tidy Windows Server 2016, which of course still has all the classic Windows server features on board.
FirstAttribute AG – Identity Management & IAM Cloud Services
We would be happy to present our services and solutions to you. Get in touch and find out how we can help you.









Leave a Reply
<p>Your email is safe with us.<br/>Information about our <a href="https://activedirectoryfaq.com/contact-us/">data protection policies</a></p>